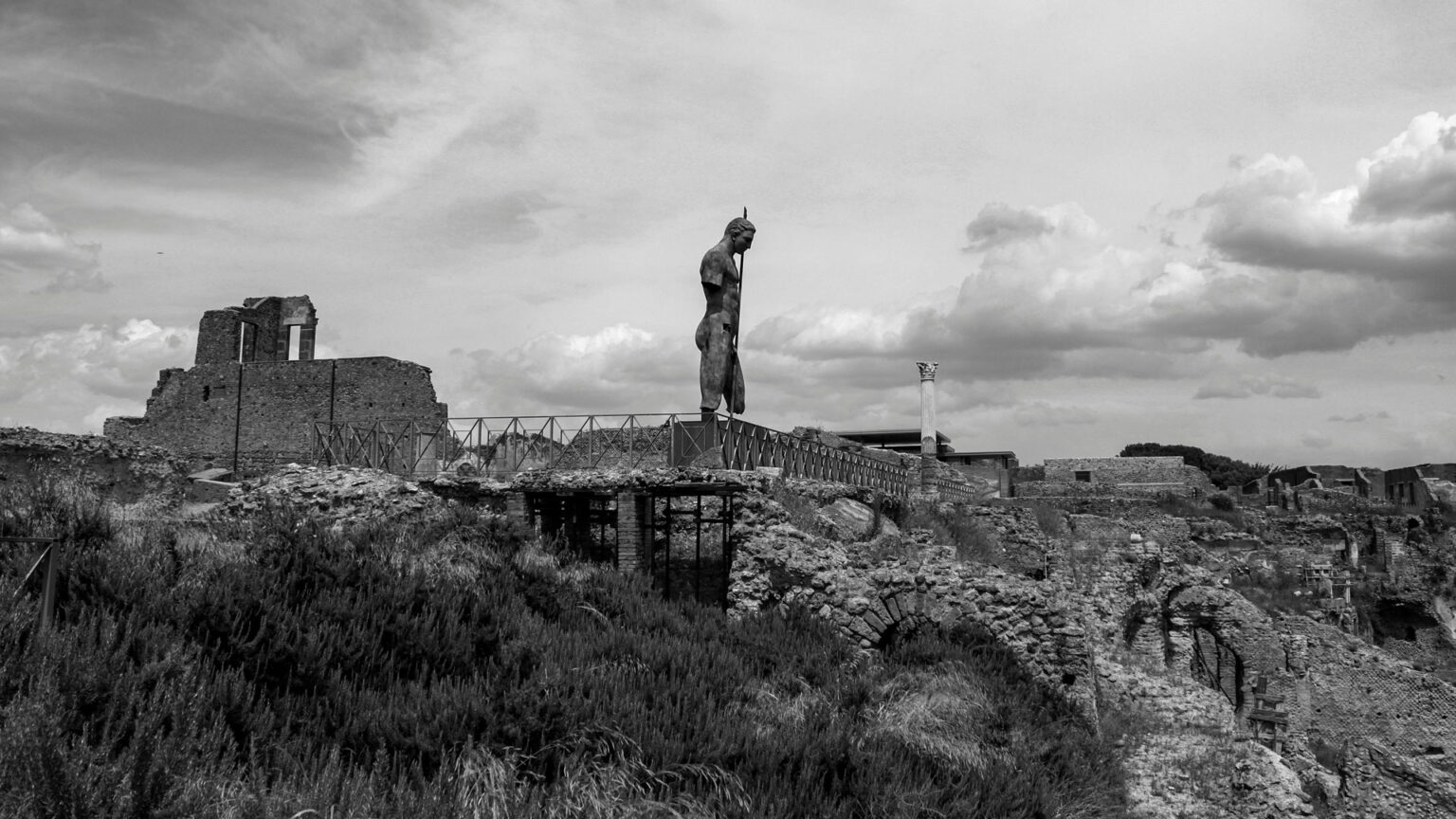
Hampi Lost City
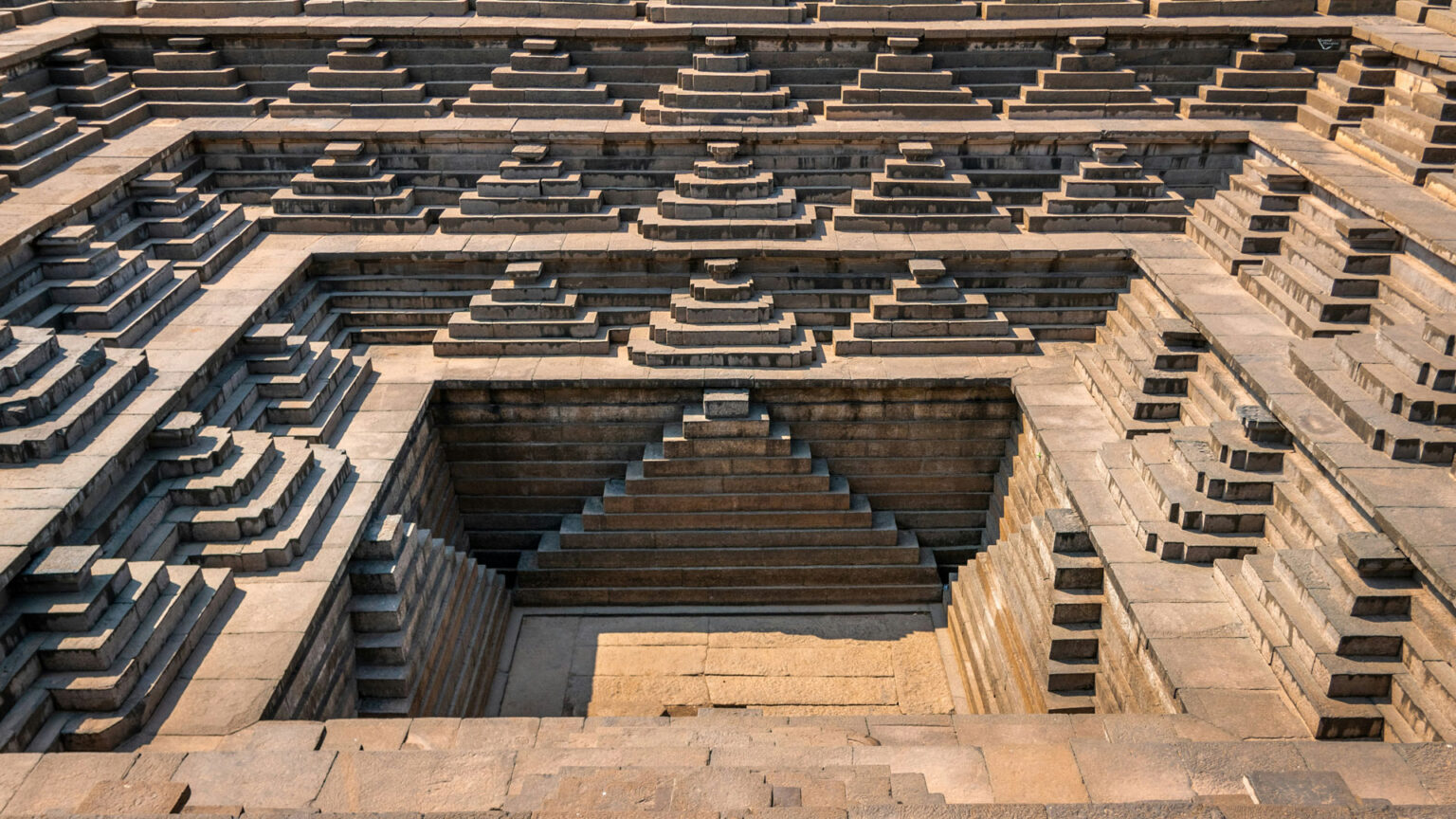
Hampi Lost City, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is a fascinating archaeological site in India’s Karnataka state. This ancient city, once the capital of the Vijayanagara Empire, is a treasure trove of history, architecture, and culture. Hampi Lost City is a sprawling complex of ancient ruins, temples, and monuments, showcasing the grandeur of India’s ancient civilizations. The city’s strategic location, nestled between the Tungabhadra River and the hills, made it an ideal place for trade and commerce. The city’s landscape is dotted with ancient ruins, each telling a story of a bygone era.
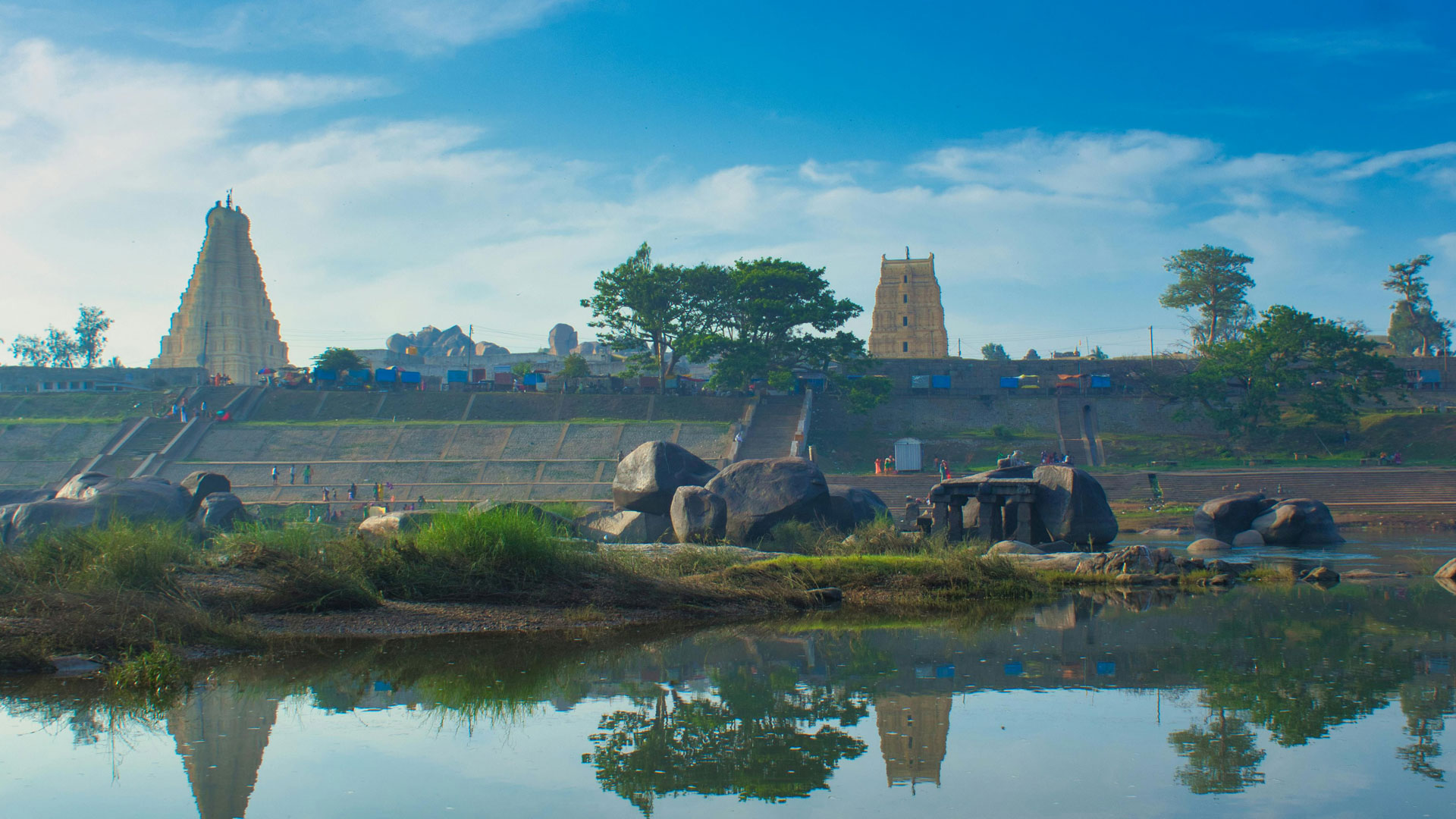

History of Hampi Lost City
Hampi Lost City has a rich history dating back to the 14th century. It was founded by Harihara and Bukka, two brothers who established the Vijayanagara Empire. The city flourished under the rule of Krishnadeva Raya, who built many of the temples and monuments that still stand today. Hampi Lost City’s history is a testament to the power and creativity of India’s ancient rulers. The city’s history can be divided into several periods, including the founding, the golden age, and the decline. The city was an important center of trade, commerce, and culture, attracting merchants and travelers from all over the world.
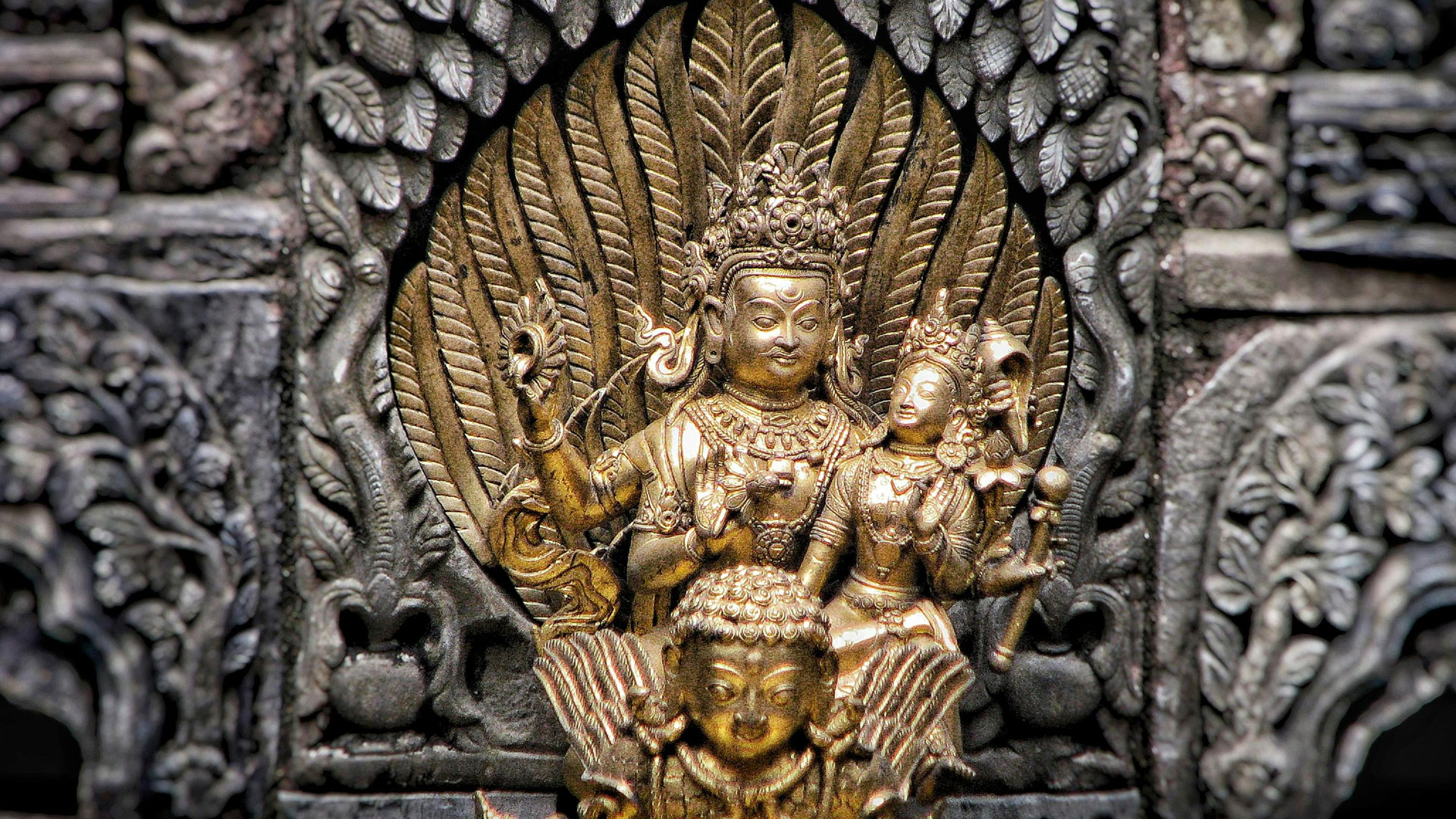

Architecture of Hampi Lost City
The architecture of Hampi Lost City is a blend of Dravidian and Vijayanagara styles. The city’s temples, palaces, and marketplaces showcase the ingenuity and craftsmanship of India’s ancient civilizations. The use of intricate carvings, pillars, and sculptures demonstrates the advanced engineering and artistic skills of the ancient Indians. The architecture of Hampi Lost City is characterized by the use of granite, sandstone, and schist, which were abundant in the region. The city’s buildings are adorned with intricate carvings, depicting scenes from Hindu mythology and everyday life.
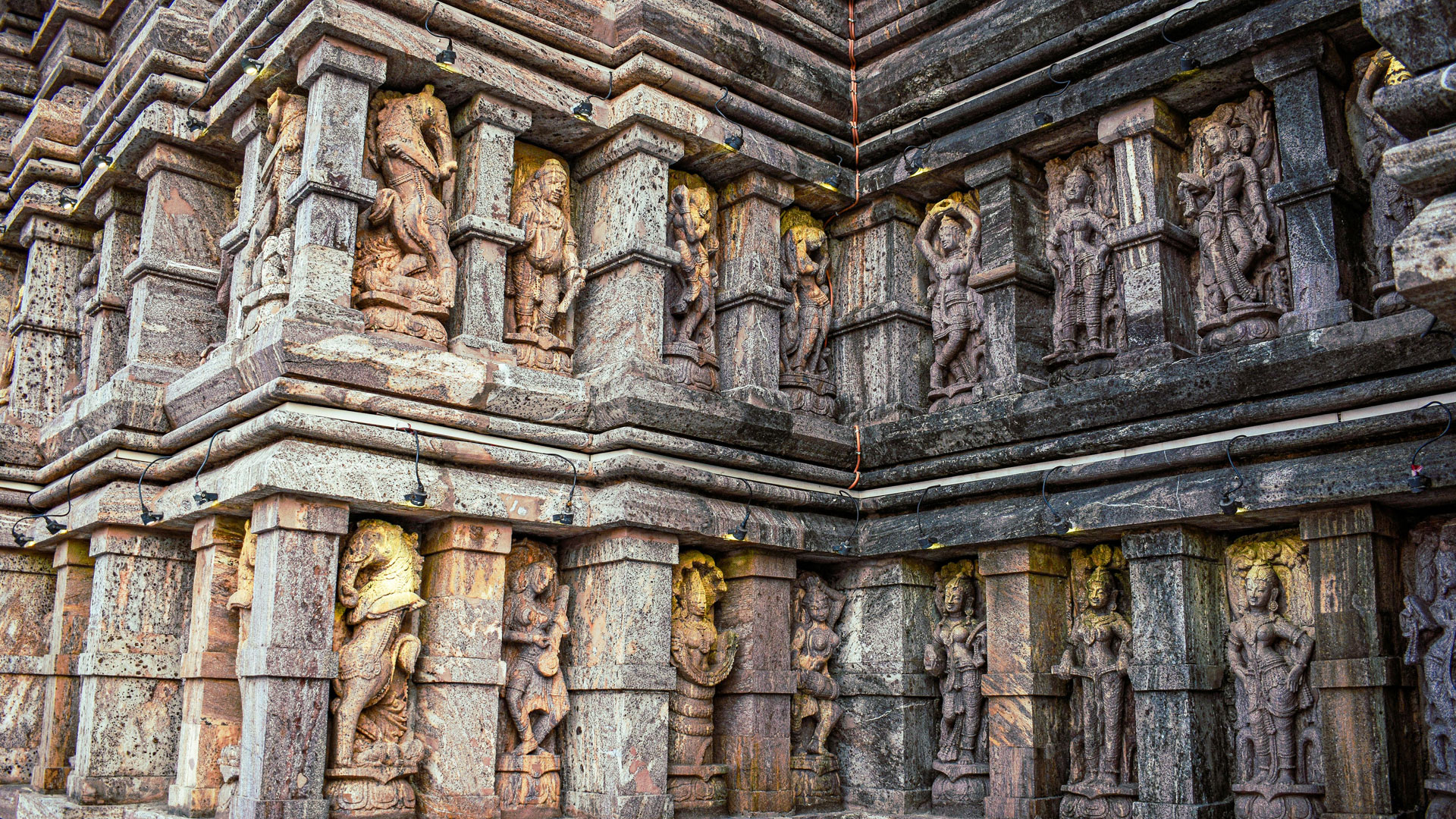

The architecture of Hampi Lost City is a unique blend of two styles:
- Dravidian style: This style is characteristic of southern Indian architecture, particularly in the Tamil Nadu region. It is known for its use of granite and sandstone, intricate carvings, and ornate sculptures.
- Vijayanagara style: This style emerged during the Vijayanagara Empire (1336-1646 CE) and is characterized by the use of granite, sandstone, and schist. It is known for its grandeur, beauty, and intricate carvings.
The city’s temples, palaces, and marketplaces showcase the ingenuity and craftsmanship of India’s ancient civilizations. The use of:
- Intricate carvings: Depicting scenes from Hindu mythology and everyday life, these carvings demonstrate the advanced artistic skills of the ancient Indians.
- Pillars: Ornate pillars support the structures, showcasing the advanced engineering skills of the ancient Indians.
- Sculptures: Intricately carved sculptures adorn the buildings, depicting scenes from Hindu mythology and everyday life.
The architecture of Hampi Lost City is characterized by the use of:
- Granite: A durable and abundant stone in the region, used for building foundations, walls, and pillars.
- Sandstone: A softer stone, used for carvings and sculptures.
- Schist: A metamorphic rock, used for building walls and pillars.
The city’s buildings are adorned with intricate carvings, depicting:
- Scenes from Hindu mythology: Stories from the Ramayana and Mahabharata epics are depicted in intricate carvings.
- Everyday life: Scenes of everyday life, such as marketplaces, royal courts, and domestic scenes, are also depicted in intricate carvings.
Virupaksha Temple
The Virupaksha Temple is a stunning example of Hampi’s architectural prowess. Built in the 7th century, it has withstood the test of time and remains an important pilgrimage site. The temple is dedicated to Lord Shiva, one of the principal deities in Hinduism.
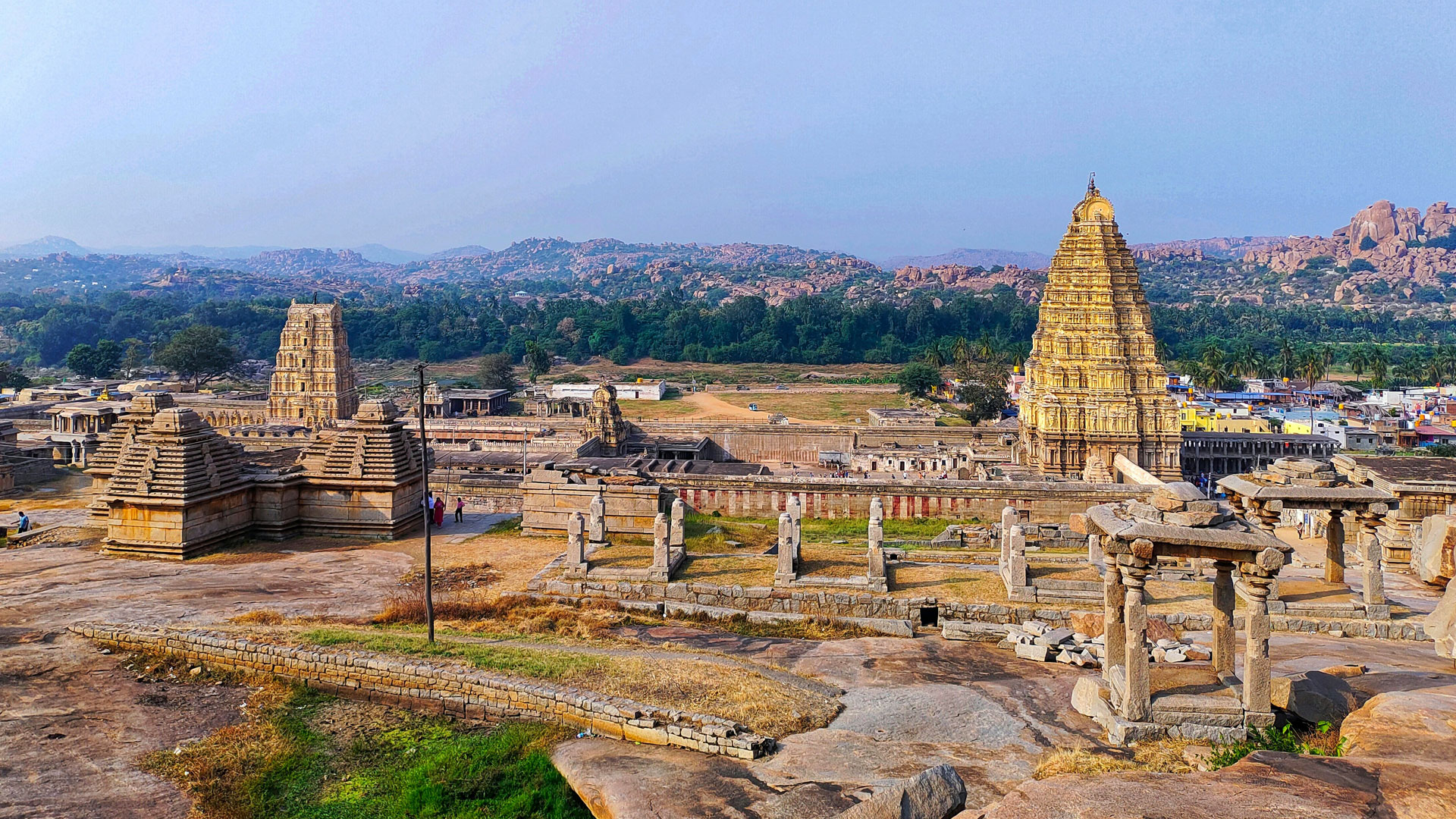

Architectural Significance
The Virupaksha Temple showcases the Vijayanagara style of architecture, characterized by:
- Grandeur and beauty
- Intricate carvings and sculptures
- Use of granite and sandstone
The temple’s design features a:
- Towering gopura (entrance tower)
- Mandapa (pillared hall)
- Garbhagriha (sanctum sanctorum)
Intricate Carvings and Sculptures
The temple’s walls and pillars are adorned with intricate carvings and sculptures, depicting scenes from Hindu mythology and everyday life. These carvings demonstrate the advanced artistic skills of the ancient Indians.
Historical Significance
The Virupaksha Temple has a rich history, dating back to the 7th century. It has been an important pilgrimage site for centuries, attracting devotees from all over India.
Preservation Efforts
The Virupaksha Temple is a protected monument under the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI). Efforts are being made to preserve and conserve this ancient wonder for future generations.
Vitthala Temple
The Vitthala Temple, dedicated to Lord Vishnu, is a magnificent monument in Hampi, Karnataka, India. This iconic temple is renowned for its intricate carvings, musical pillars, and stunning architecture, showcasing the Vijayanagara style of building design. The temple’s grandeur and beauty make it a standout attraction in Hampi, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
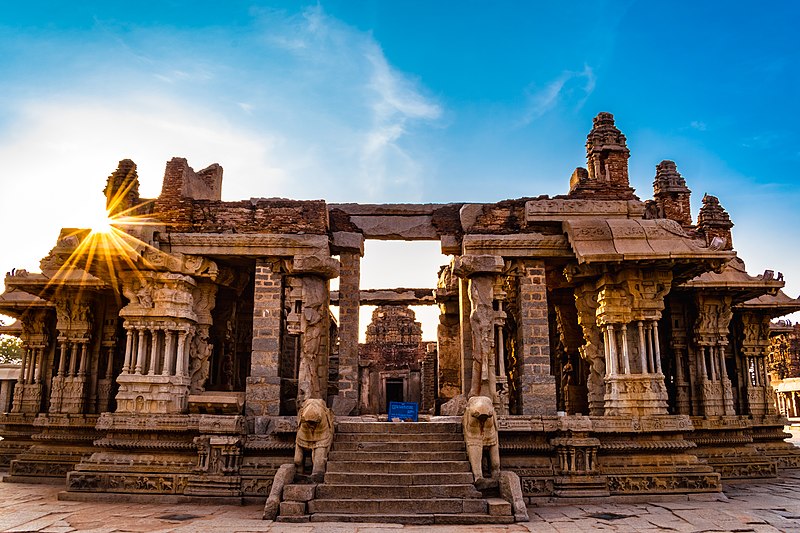

Architectural Significance
The Vitthala Temple’s design exemplifies the Vijayanagara style of architecture, characterized by:
- Grandeur and beauty
- Intricate carvings and sculptures
- Use of granite and sandstone
- Musical pillars
The temple’s layout features a:
- Towering gopura (entrance tower)
- Mandapa (pillared hall)
- Garbhagriha (sanctum sanctorum)
Intricate Carvings and Sculptures
The temple’s walls and pillars are adorned with intricate carvings and sculptures, depicting scenes from Hindu mythology and everyday life. These carvings demonstrate the advanced artistic skills of the ancient Indians.
Musical Pillars
The Vitthala Temple’s musical pillars are a unique feature, producing different musical notes when tapped. These pillars are made of granite and are arranged in a specific pattern to create a musical effect.
History and Significance
The Vitthala Temple was built in the 16th century during the reign of King Krishnadeva Raya, one of the most powerful rulers of the Vijayanagara Empire. The temple is dedicated to Lord Vishnu, one of the principal deities in Hinduism.
Preservation and Conservation
The Vitthala Temple is a protected monument under the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI). Efforts are being made to preserve and conserve this ancient wonder for future generations.
Festivals and Celebrations
The Vitthala Temple celebrates several festivals throughout the year, including the annual Vitthala Temple Festival, which attracts thousands of devotees. Other significant festivals celebrated at the temple include Vaikuntha Ekadashi and Rama Navami.
Hampi’s Landscape
Hampi Lost City’s landscape is dotted with ancient ruins, each telling a story of a bygone era. The city’s strategic location, nestled between the Tungabhadra River and the hills, made it an ideal place for trade and commerce. The surrounding hills and valleys offer breathtaking views of the ancient city.
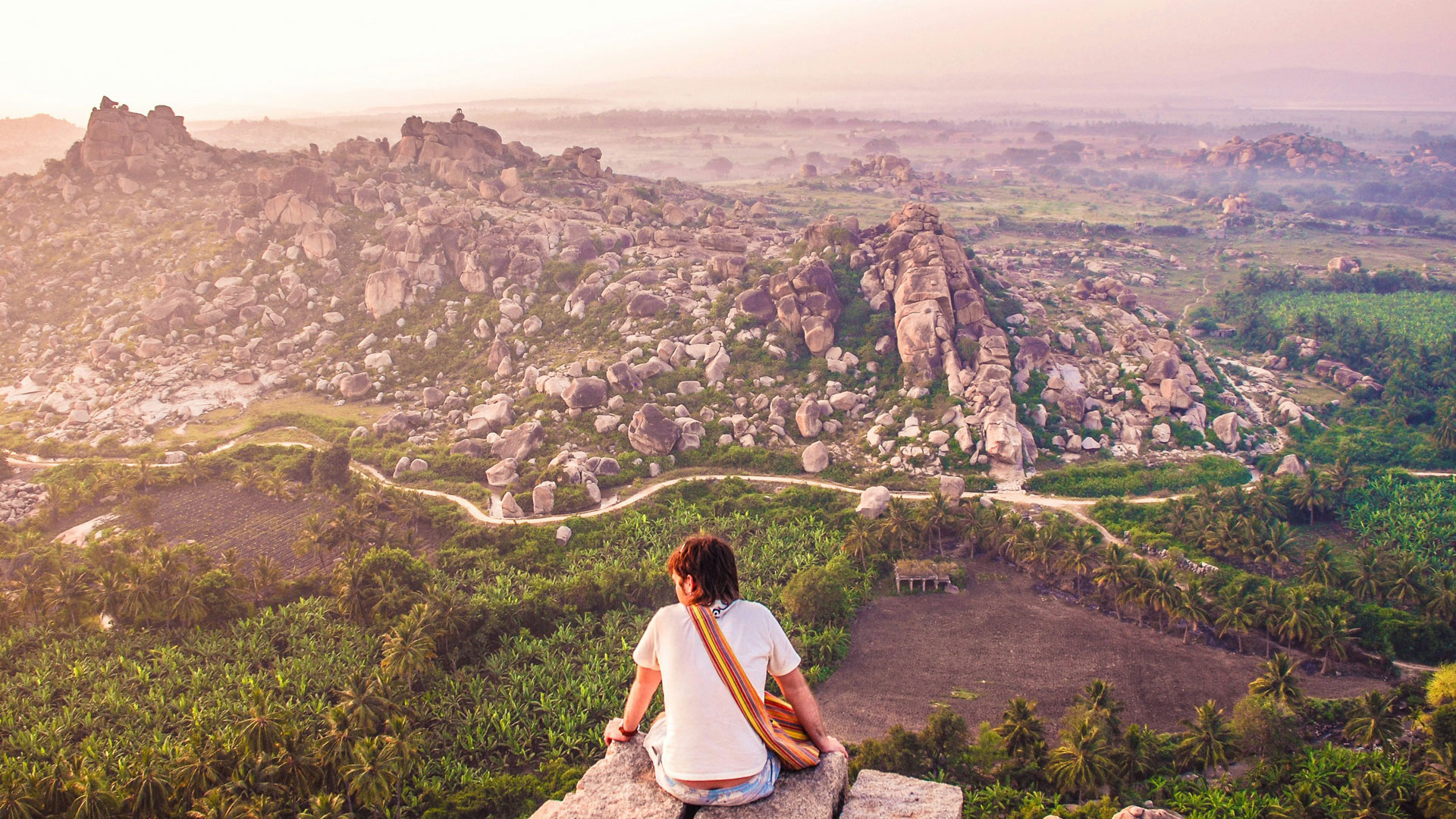

Hampi’s Landscape refers to the natural and man-made features that surround the ancient city of Hampi, also known as the Lost City. Here’s a more detailed explanation:
Ancient Ruins
The landscape is dotted with ancient ruins, including:
- Temples
- Palaces
- Marketplaces
- Fortifications
- Monuments
Each ruin tells a story of the city’s rich history, showcasing the architectural styles, cultural practices, and artistic achievements of the Vijayanagara Empire.
Strategic Location
Hampi’s location between the Tungabhadra River and the hills made it an ideal place for:
- Trade: The river provided a means of transportation, connecting Hampi to other regions.
- Commerce: The city’s location facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures.
Surrounding Hills and Valleys
The hills and valleys surrounding Hampi offer:
- Breathtaking views: Panoramic views of the ancient city and its ruins.
- Natural beauty: The landscape is dotted with trees, rocks, and other natural features.
- Historical significance: The hills and valleys may have played a role in the city’s defense, trade, and cultural practices.
Unique Features
Hampi’s landscape is unique due to:
- The combination of natural and man-made features.
- The city’s strategic location, which contributed to its prosperity.
- The well-preserved ancient ruins, which provide a glimpse into the past.
Importance
Hampi’s landscape is important because:
- It showcases the city’s rich history and cultural heritage.
- It provides a unique glimpse into the lives of the people who lived there.
- It is a testament to the architectural, artistic, and engineering achievements of the Vijayanagara Empire.
Trade and Commerce
Hampi Lost City was an important center of trade and commerce in ancient India. Merchants from all over the world came to Hampi to buy and sell goods like spices, textiles, and precious stones. The city’s marketplaces, like the Courtesan Street, showcase the bustling commercial activity of the past.
Hampi was a thriving commercial hub in ancient India, attracting merchants from far and wide. Here’s a more detailed explanation:
Importance of Trade and Commerce
Hampi’s strategic location between the Tungabhadra River and the hills made it an ideal center for trade and commerce. The city’s marketplaces were bustling with activity, with merchants buying and selling a variety of goods.
Goods Traded
Some of the goods traded in Hampi’s marketplaces included:
- Spices: Like pepper, cardamom, and cloves
- Textiles: Fine silks, cotton, and woolen fabrics
- Precious stones: Diamonds, rubies, and emeralds
- Metals: Gold, silver, and copper
- Agricultural products: Grains, pulses, and sugarcane
Marketplaces
Hampi’s marketplaces, like the Courtesan Street, were famous for their commercial activity. These marketplaces were:
- Well-planned and organized
- Filled with shops, stalls, and warehouses
- Bustling with merchants, traders, and customers
Courtesan Street
Courtesan Street, in particular, was a famous marketplace in Hampi. It was lined with:
- Shops selling fine silks, textiles, and precious stones
- Stalls offering spices, metals, and agricultural products
- Warehouses storing goods for trade and commerce
Merchants and Traders
Merchants and traders from all over the world came to Hampi to buy and sell goods. They included:
- Indian merchants from nearby regions
- Foreign traders from China, Arabia, and Europe
- Local artisans and craftsmen selling their wares
Trade Routes
Hampi was connected to other trade centers through a network of trade routes, including:
- The Silk Road
- The Spice Route
- The Arabian Sea trade route
These trade routes enabled the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures between Hampi and other civilizations.
Cultural Significance
Hampi Lost City is a cultural treasure trove, showcasing India’s rich heritage. The city’s temples, palaces, and monuments are a testament to the country’s architectural, artistic, and literary achievements. Hampi’s cultural significance extends beyond India, making it a vital part of world heritage.

Cultural Treasure Trove
Hampi Lost City is a cultural treasure trove, showcasing India’s rich heritage through its:
- Temples: Representing India’s architectural and artistic achievements
- Palaces: Symbolizing the country’s royal and imperial past
- Monuments: Honoring India’s literary and cultural icons
Architectural Achievements
Hampi’s temples and palaces demonstrate India’s architectural achievements, including:
- Dravidian style architecture
- Vijayanagara style architecture
- Blend of Hindu, Islamic, and European influences
Artistic Achievements
The city’s temples, palaces, and monuments showcase India’s artistic achievements, including:
- Intricate carvings and sculptures
- Ornate paintings and murals
- Beautiful calligraphy and inscriptions
Literary Achievements
Hampi has a rich literary heritage, with the city being a hub for scholars, poets, and writers. The city’s cultural significance extends to its:
- Ancient texts and manuscripts
- Literary works in Sanskrit, Kannada, and Telugu
- Influence on Indian literature and poetry
World Heritage
Hampi’s cultural significance extends beyond India, making it a vital part of world heritage. The city’s:
- Unique blend of cultures and influences
- Architectural and artistic innovations
- Literary and intellectual contributions
make it a significant cultural site, recognized by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site.
Iconic Symbols
Hampi’s cultural significance is also reflected in its iconic symbols, including:
- The Virupaksha Temple
- The Vitthala Temple
- The Lotus Mahal
- The Elephant Stables
These symbols represent India’s rich cultural heritage and its contributions to world culture.