McMurdo Station: Gateway to Antarctic Research
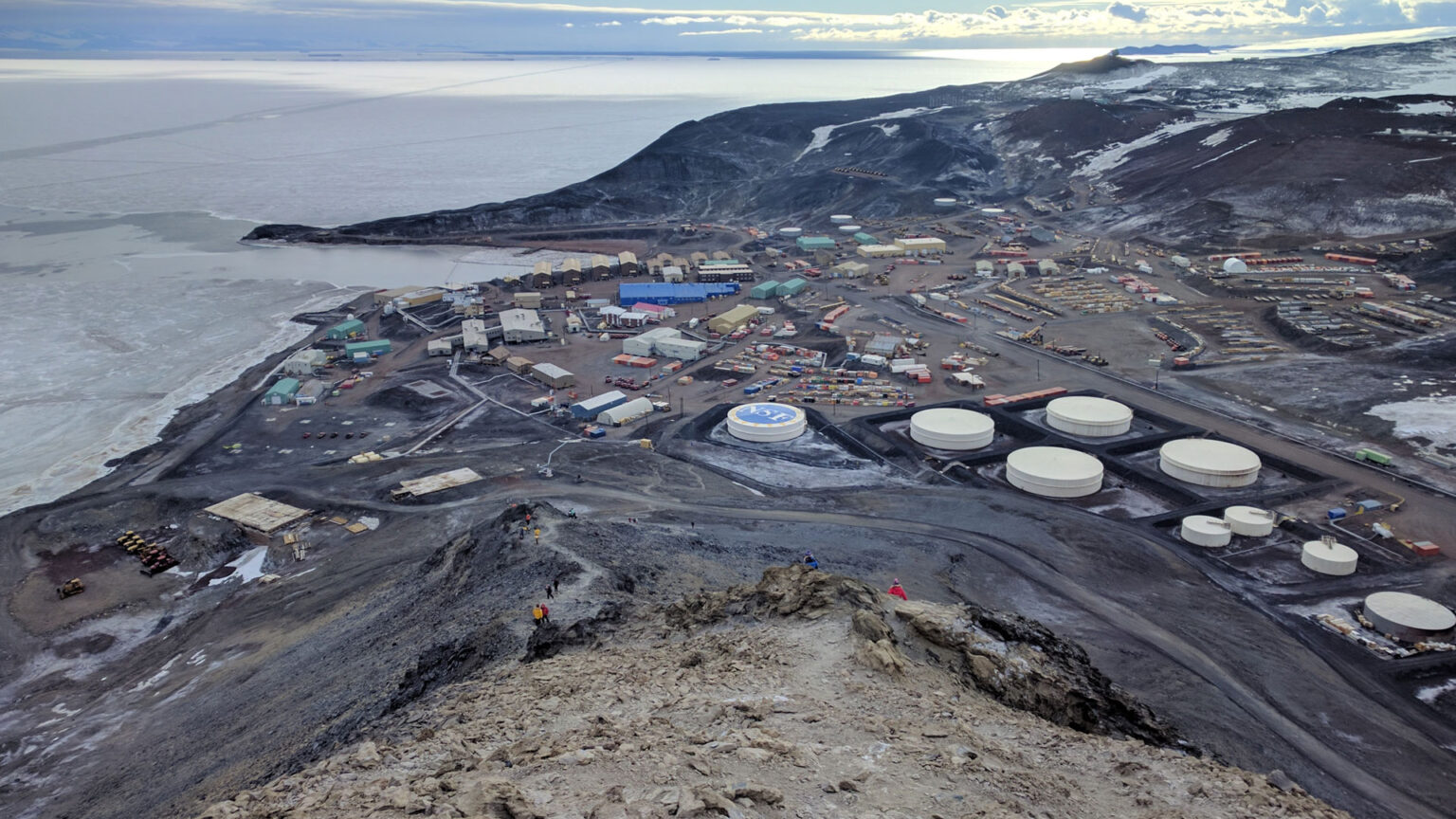
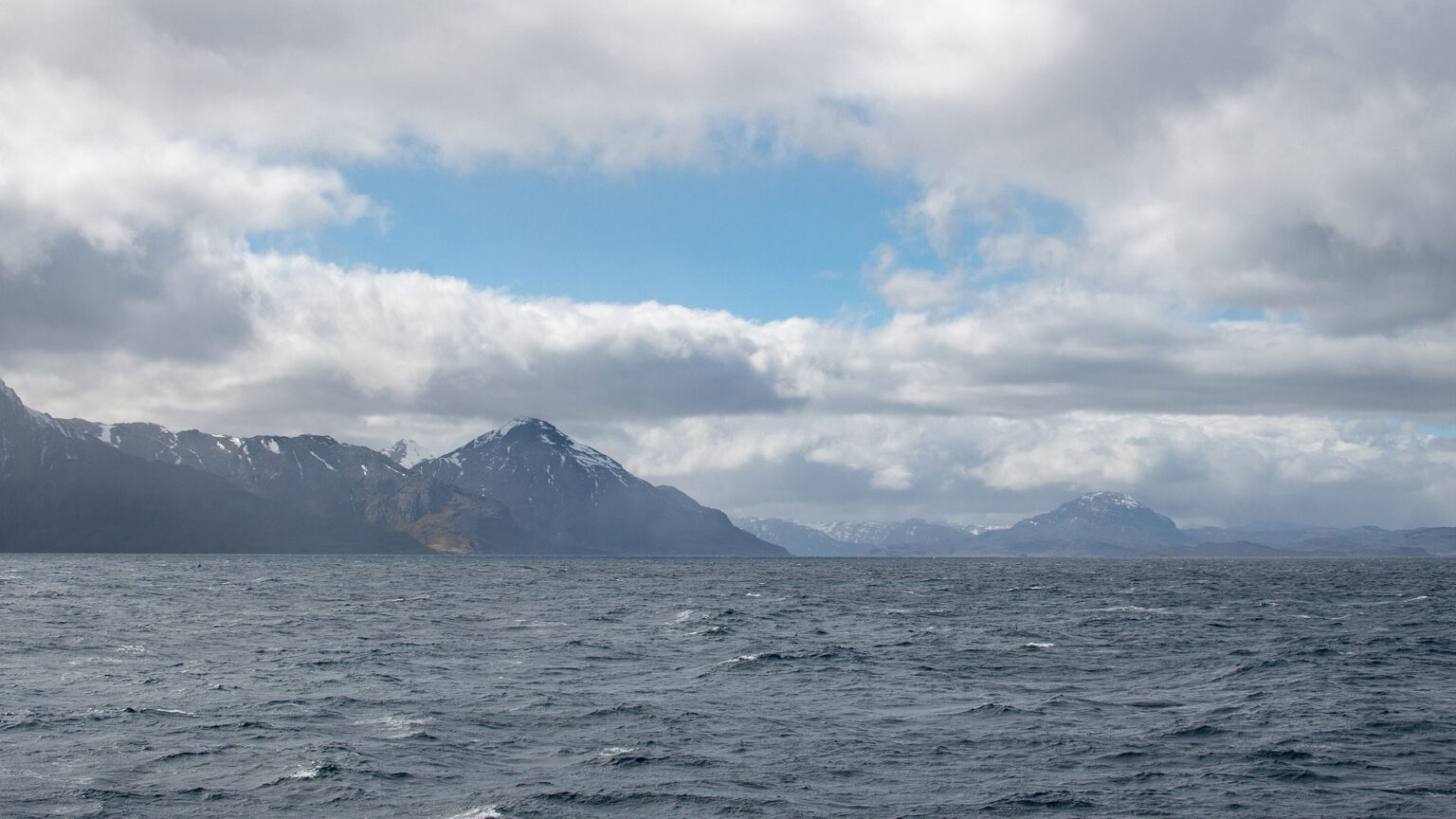
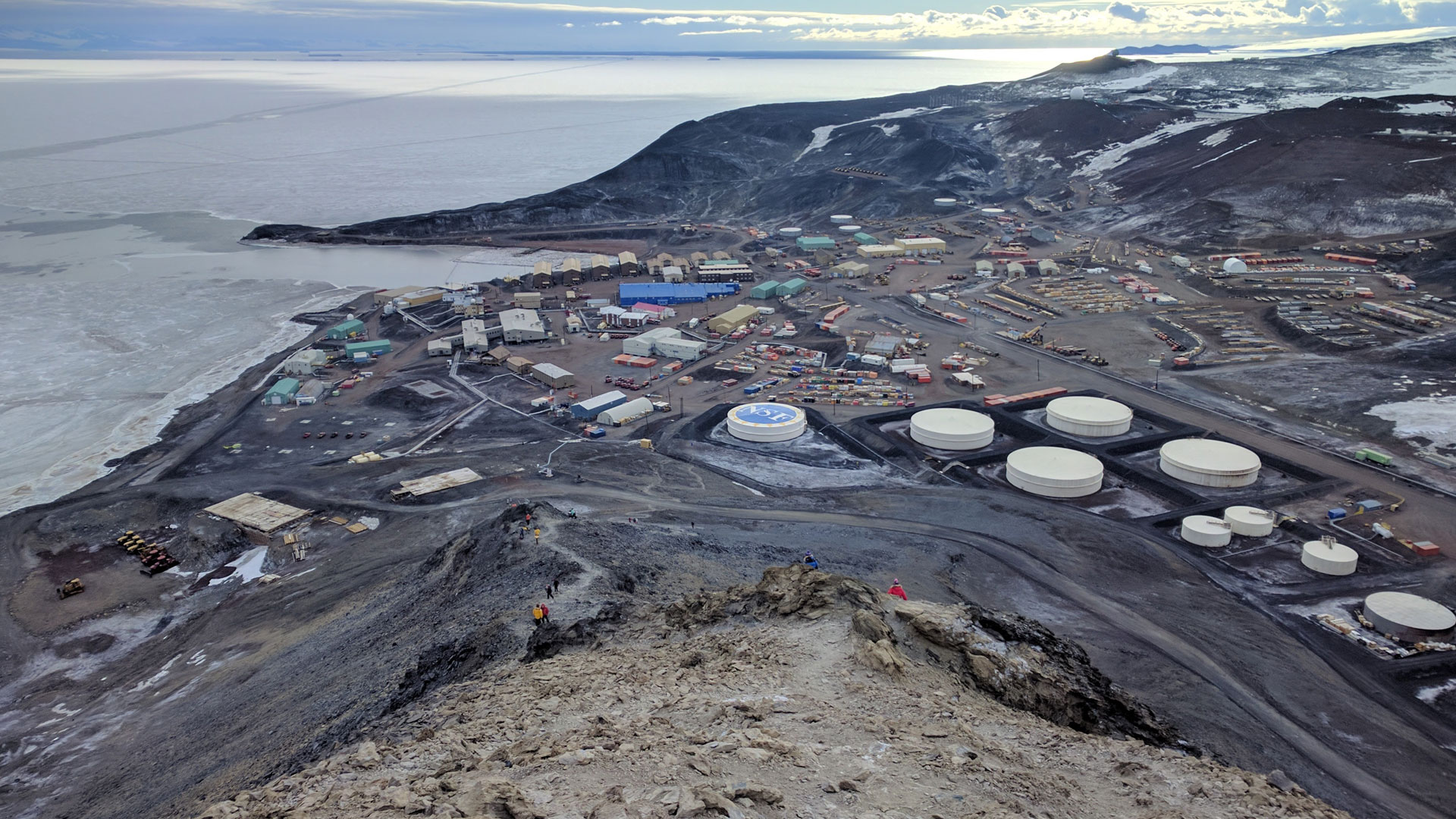
Located on the southern tip of Ross Island, Antarctica, McMurdo Station is one of the most remote and fascinating research stations on Earth. Established in 1955, this United States research facility has been at the forefront of Antarctic scientific exploration for over six decades. McMurdo Station serves as a critical hub for scientists, researchers, and support staff, enabling groundbreaking research in one of the world’s most extreme environments.

Strategic Importance
McMurdo Station plays a vital role in advancing our understanding of Antarctica’s unique ecosystem, geology, and climate. The station’s proximity to the South Pole and the Antarctic Circle makes it an ideal location for studying the continent’s extreme weather patterns, geological features, and wildlife. Research conducted at McMurdo Station contributes significantly to our knowledge of climate change, astronomy, geology, and biology.
Unique Features
McMurdo Station boasts several unique features that facilitate cutting-edge research:
- Research facilities: State-of-the-art laboratories, greenhouses, and observatories support a wide range of scientific disciplines.
- Logistical support: A 3,000-foot airstrip, seaport, and nearby Scott Base (New Zealand) enable efficient transportation and supply chain management.
- Diverse landscape: McMurdo Station is surrounded by a diverse range of Antarctic landscapes, including glaciers, mountains, and sea ice.
- International collaboration: Researchers from around the world collaborate at McMurdo Station, fostering global scientific cooperation.
As we delve into the world of McMurdo Station, we’ll explore its rich history, scientific discoveries, and daily life at this extraordinary research facility.
Establishment and Development (1955-1960)
McMurdo Station was established in 1955 as part of Operation Deep Freeze, a United States Navy expedition to Antarctica. The station was originally designed to support scientific research and provide logistical support for the U.S. Antarctic Program. The first commander, Rear Admiral Richard E. Byrd, oversaw the construction of the station, which was built on the site of a former British research station. The location was chosen for its accessibility by sea and air, as well as its proximity to the South Pole.
The construction of McMurdo Station was a significant undertaking, requiring the transportation of materials and personnel to one of the most remote locations on Earth. The U.S. Navy’s Seabees, a construction battalion, played a crucial role in building the station’s infrastructure, including barracks, laboratories, and support facilities. The station’s early years were marked by challenges, including harsh weather conditions, logistical difficulties, and limited resources.
Key Milestones and Achievements
1. 1955: McMurdo Station is Established
McMurdo Station was officially established on December 16, 1955, with the arrival of the first personnel. The station’s initial purpose was to support scientific research and provide logistical support for the U.S. Antarctic Program.
2. 1957: Scientific Research Programs Begin
The station’s first scientific research programs began in 1957, focusing on geology, biology, and physics. Researchers conducted fieldwork, collected data, and analyzed samples, laying the foundation for future research.
3. 1958: Airstrip Construction
The U.S. Navy constructed a 3,000-foot airstrip, enabling the transportation of personnel and cargo by air. This significantly improved the station’s accessibility and facilitated research operations.
4. 1960: Permanent Research Facility
McMurdo Station became a permanent research facility in 1960, with the U.S. Antarctic Program committing to long-term research and operations.
5. 1961: First American Expedition to the South Pole
McMurdo Station supported the first American expedition to reach the South Pole, led by Rear Admiral Richard E. Byrd.
6. 1970s: Expansion and Modernization
During the 1970s, McMurdo Station underwent significant expansion and modernization. New research facilities, laboratories, and support infrastructure were constructed, enabling more complex and diverse research programs.
7. 1980s: International Cooperation
McMurdo Station played a critical role in international scientific collaborations during the 1980s. Researchers from around the world worked together on projects, sharing resources and expertise.
8. 1990s: Renovations and Modernization
In the 1990s, McMurdo Station underwent significant renovations and modernization. The station’s infrastructure was upgraded, and new research facilities were constructed to support cutting-edge research.
Historical Significance
McMurdo Station has played a pivotal role in advancing our understanding of Antarctica and the global environment. Some notable achievements include:
1. Climate Change Research
McMurdo Station has contributed significantly to climate change research, providing valuable data on Antarctic ice cores and atmospheric conditions. Researchers have studied the station’s unique ice cores, providing insights into Earth’s climate history.
2. Geological Discoveries
Researchers at McMurdo Station have made groundbreaking discoveries about Antarctica’s geological history, including the discovery of ancient fossils. These findings have shed light on Earth’s evolution and the continent’s formation.
3. Astronomical Research
The station’s unique location and low-light conditions make it an ideal location for astronomical research. Scientists have conducted research on cosmic microwave background radiation, dark matter, and other phenomena.
4. International Cooperation
McMurdo Station has fostered international scientific collaboration, hosting researchers from over 20 countries. This cooperation has facilitated the sharing of resources, expertise, and knowledge.
Challenges and Controversies
Despite its achievements, McMurdo Station has faced challenges and controversies, including:
1. Environmental Concerns
The station’s presence has raised concerns about environmental impact and waste management. Efforts have been made to minimize the station’s footprint and mitigate environmental harm.
2. Logistical Challenges
McMurdo Station’s remote location poses significant logistical challenges. Transportation, communication, and supply chain management are ongoing challenges.
3. Funding
The station has faced funding uncertainties and budget constraints, impacting research programs and operations.
Living Conditions and Challenges
Life at McMurdo Station is unique and challenging, requiring adaptability and resilience. Researchers and support staff face:
- Extreme Weather: Temperatures range from -40°C to 10°C (-40°F to 50°F), with winds reaching 100 km/h (62 mph). Blizzards and storms can last for days, isolating the station.
- Isolation: The station is inaccessible by land, with limited communication and transportation options. Residents rely on satellite communications and occasional flights.
- Confined Living Spaces: Dormitories and living quarters are cramped, with shared facilities. Privacy is limited, and personal space is precious.
- Limited Amenities: No permanent residents, limited shopping, and restricted entertainment options. Residents must bring personal items and entertainment.
- Physical Demands: Researchers often work in extreme conditions, requiring physical stamina and endurance.
Daily Life and Routines
Despite challenges, daily life at McMurdo Station is structured and routine-oriented:
- Work Schedules: Researchers and support staff work varied shifts, often 6-day weeks. Flexibility is essential, as research demands and weather conditions change.
- Meal Times: Community meals are served at designated times, providing social interaction and structure.
- Recreation: Gym, library, and recreational activities available, promoting physical and mental well-being.
- Social Events: Regular gatherings, movie nights, and celebrations foster community spirit.
- Personal Time: Residents prioritize personal time, pursuing hobbies, reading, or relaxation.
Support Staff and Services
McMurdo Station relies on dedicated support staff and services:
- Medical Team: Providing medical care and emergency services, including telemedicine.
- Culinary Team: Preparing meals for residents, accommodating dietary needs.
- Maintenance Crew: Ensuring infrastructure and equipment functionality.
- Communication Team: Managing communication networks and IT services.
- Mental Health Support: Access to counseling and wellness programs.
Community and Morale
To maintain morale and community spirit:
- Volunteer Programs: Residents participate in community events and projects.
- Recreational Activities: Hiking, skiing, and outdoor pursuits.
- Social Clubs: Formed around shared interests.
- Mental Health Support: Access to counseling and wellness programs.
- Community Events: Celebrations, movie nights, and gatherings.
Living Quarters and Facilities
McMurdo Station’s living quarters and facilities include:
- Dormitories: Shared and private rooms.
- Galley (Kitchen): Community dining area.
- Recreation Room: Leisure activities and socializing.
- Gym and Fitness Center: Exercise equipment and classes.
- Library and Resource Center: Access to books, media, and research materials.
- Medical Facility: Providing medical care and emergency services.
- Communication Center: Managing communication networks and IT services.
Challenges and Opportunities
Living at McMurdo Station presents unique challenges and opportunities:
- Personal Growth: Overcoming adversity and developing resilience.
- Professional Development: Collaborating with international researchers.
- Community Building: Forming strong bonds with colleagues.
- Isolation and Confined Spaces: Managing mental and physical health.
- Research Opportunities: Contributing to groundbreaking research.
Wildlife in Antarctica
Antarctica’s unique and diverse wildlife thrives in the harsh, extreme environment surrounding McMurdo Station. The region is home to:
- Penguins: Adelie, Chinstrap, Gentoo, and Emperor penguins inhabit the region, with colonies on Ross Island and surrounding areas.
- Seals: Weddell, Crabeater, and Leopard seals are common in Antarctic waters, often spotted near McMurdo Station.
- Whales: Humpback, Minke, and Orca whales migrate through Antarctic waters, feeding on krill and small fish.
- Seabirds: Albatrosses, Petrels, and Skuas are abundant, nesting on rocky outcrops and islands.
Conservation Efforts
To protect Antarctica’s fragile ecosystem, international agreements and organizations are in place:
- Antarctic Treaty System: Regulates human activity, ensuring environmental protection and preserving the continent’s natural resources.
- Protocol on Environmental Protection: Prevents pollution, habitat destruction, and promotes sustainable tourism.
- International Association of Antarctica Expedition Cruise Operators (IAATO): Promotes responsible tourism, supporting conservation efforts.
Environmental Protection
McMurdo Station implements measures to minimize its environmental footprint:
- Waste Management: Recycling, composting, and proper waste disposal minimize waste impact.
- Energy Efficiency: Renewable energy sources, reduced energy consumption, and energy-efficient infrastructure.
- Water Conservation: Efficient water use, wastewater treatment, and water recycling.
Research and Monitoring
Scientists at McMurdo Station conduct research and monitoring to understand and mitigate environmental impacts:
- Climate Change Impacts: Studying effects on wildlife, ecosystems, and sea-level rise.
- Species Populations: Tracking penguin, seal, and whale populations to inform conservation efforts.
- Habitat Preservation: Protecting unique Antarctic ecosystems, including ice-free areas and coastal regions.
Conservation Challenges
Despite efforts, conservation challenges persist:
- Climate Change: Impacts on wildlife habitats, populations, and ecosystems.
- Human Impact: Pollution, habitat destruction, and disturbance from human activity.
- Invasive Species: Preventing non-native species introduction, protecting Antarctica’s unique biodiversity.
Conservation Successes
Conservation efforts have achieved notable successes:
- Protected Areas: Establishment of protected areas, including national parks and wildlife reserves.
- Species Recovery: Conservation efforts have contributed to population recoveries, such as the Adelie penguin.
- International Cooperation: Collaboration among nations, organizations, and researchers.
Logistical Challenges
Operating in Antarctica poses significant logistical challenges that impact research operations:
- Remote Location: Accessing McMurdo Station requires complex transportation arrangements, involving flights, ships, and helicopters.
- Harsh Environment: Extreme weather conditions, including temperatures below -40°C (-40°F) and winds over 100 km/h (62 mph), impact research operations.
- Limited Infrastructure: McMurdo Station’s infrastructure requires constant maintenance to ensure functionality.
- Supply Chain Management: Ensuring timely delivery of essential supplies, including food, fuel, and research equipment.
- Communication Challenges: Overcoming communication barriers due to remote location, limited internet connectivity, and satellite communication reliance.
Scientific Opportunities
Despite challenges, McMurdo Station offers unparalleled scientific opportunities:
- Unique Ecosystems: Studying Antarctica’s diverse and extreme ecosystems, including ice-free regions, glaciers, and marine ecosystems.
- Climate Change Research: Investigating climate change impacts on ice sheets, glaciers, and sea-level rise.
- Astrophysics and Astronomy: Leveraging the clear, dark skies for astronomical research, including cosmic microwave background radiation studies.
- Geological Research: Exploring Antarctica’s geological history, including fossil records and geological mapping.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Protecting and studying Antarctica’s unique wildlife, including penguins, seals, and whales.
Future Research Directions
Future research at McMurdo Station will focus on:
- Climate Change Mitigation: Investigating strategies to mitigate climate change impacts on Antarctica and globally.
- Renewable Energy: Developing sustainable energy solutions for McMurdo Station and beyond.
- Advanced Technologies: Integrating cutting-edge technologies for research, including drones, autonomous vehicles, and sensors.
- International Collaboration: Enhancing global scientific cooperation and knowledge sharing.
- Interdisciplinary Research: Integrating multiple disciplines for holistic understanding of complex systems.
Opportunities for Growth
McMurdo Station’s future holds opportunities for growth:
- Expanding Research Capabilities: Enhancing facilities and infrastructure to support new research initiatives.
- Diversifying Research Disciplines: Incorporating new fields of study, such as biology, geology, and astronomy.
- Enhancing International Cooperation: Strengthening global partnerships and collaborations.
- Developing Sustainable Practices: Implementing environmentally friendly operations and reducing waste.
- Inspiring Future Generations: Educating and training the next generation of researchers and scientists.
Challenges and Opportunities Balance
While challenges exist, McMurdo Station’s opportunities for scientific discovery and growth outweigh them:
- Balancing Research and Logistics: Managing resources to support research while maintaining logistical operations.
- Overcoming Obstacles: Finding creative solutions to overcome challenges.
- Embracing Innovation: Integrating new technologies and approaches.
- Fostering Collaboration: Building strong relationships among researchers, support staff, and international partners.
- Advancing Knowledge: Contributing to the global understanding of Antarctica and the Earth’s systems.
Conclusion
McMurdo Station stands as a testament to human curiosity and scientific inquiry. This remote research station on Ross Island, Antarctica, plays a vital role in advancing our understanding of the Earth’s systems, climate change, and the universe.
Summary of McMurdo Station’s Significance
McMurdo Station:
- Supports cutting-edge research in astronomy, geology, biology, and climate science.
- Facilitates international scientific collaboration.
- Contributes to our understanding of Antarctica’s unique ecosystems.
- Provides insights into climate change impacts.
- Advances our knowledge of the Earth’s systems.
Call to Action
As we continue to explore and learn from McMurdo Station, we invite you to:
- Learn more about McMurdo Station’s research initiatives.
- Support scientific research and conservation efforts.
- Stay informed about climate change and its impacts.
- Inspire future generations to pursue careers in science.
- Explore the wonders of Antarctica through documentaries, books, and online resources.
Together, we can advance our understanding of the Earth and the universe.